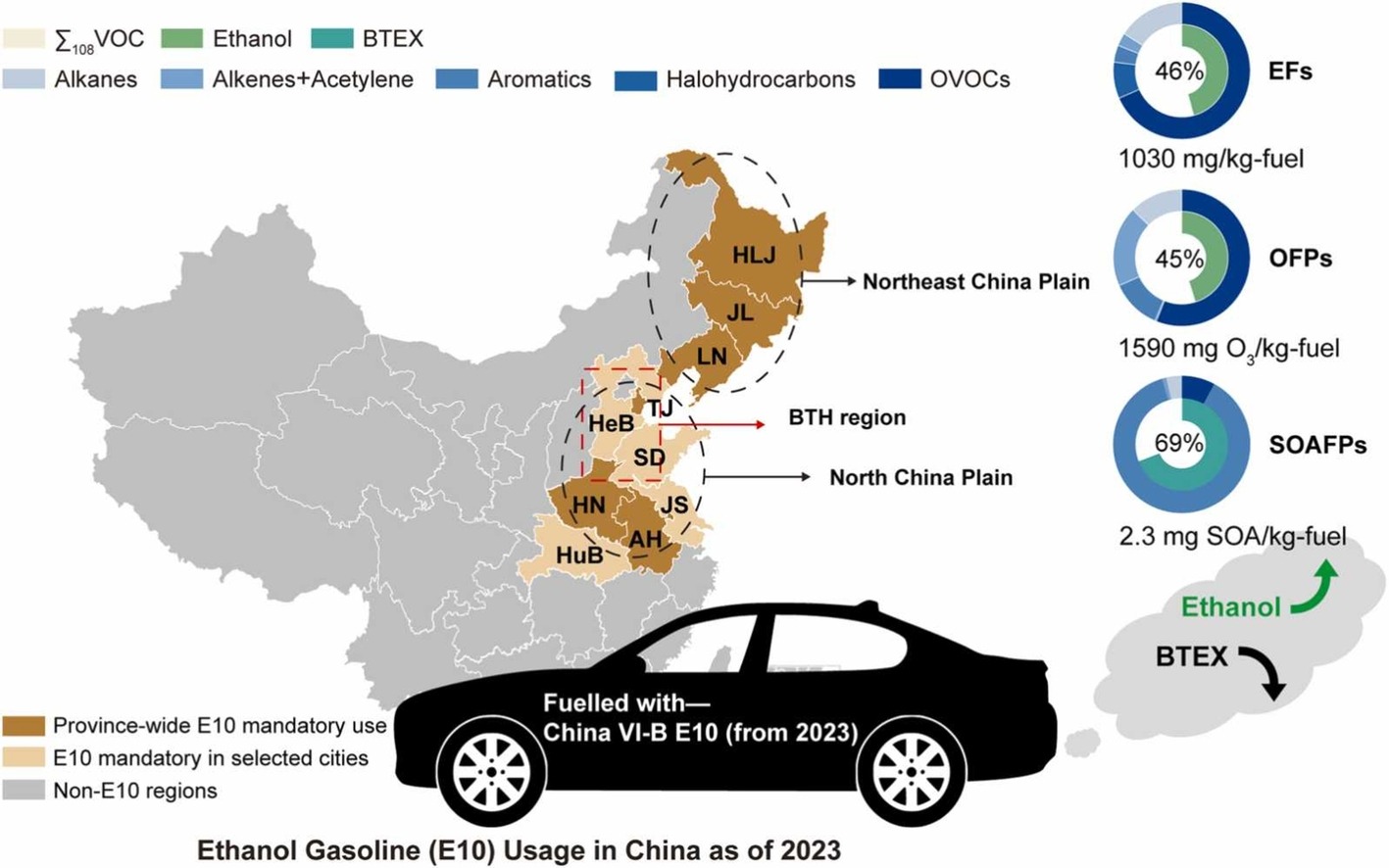
On January 31, Ziyang’s paper ‘Real-world VOCs from ethanol gasoline vehicles: Speciation, ozone formation potential, and inter-city differences‘ has been published in JHM. Congratulations!
所有由Gan Zhang发布的文章
Buqing and Pingyang completed their PDRA
On January 16 and 29, Buqing and Pingyang have reports on their PDRA, respectively, over the assessment committees. Both of them did good jobs and contributed to the development of the group and the State Kay Laboratory. Specifically, Buqing pioneers in compound-specific radiocarbon analysis (CSRA) of molecular organic tracers in the environment, and Pingyang joined to pioneer the measurement and application of 14CO2 for urban and regional green house monitoring and audit. Buqing becomes a research staff in the institute, and Pingyang going to work in Guangxi Academy of Environmental Sciences. We hope them a better future.
Beibu Gulf University
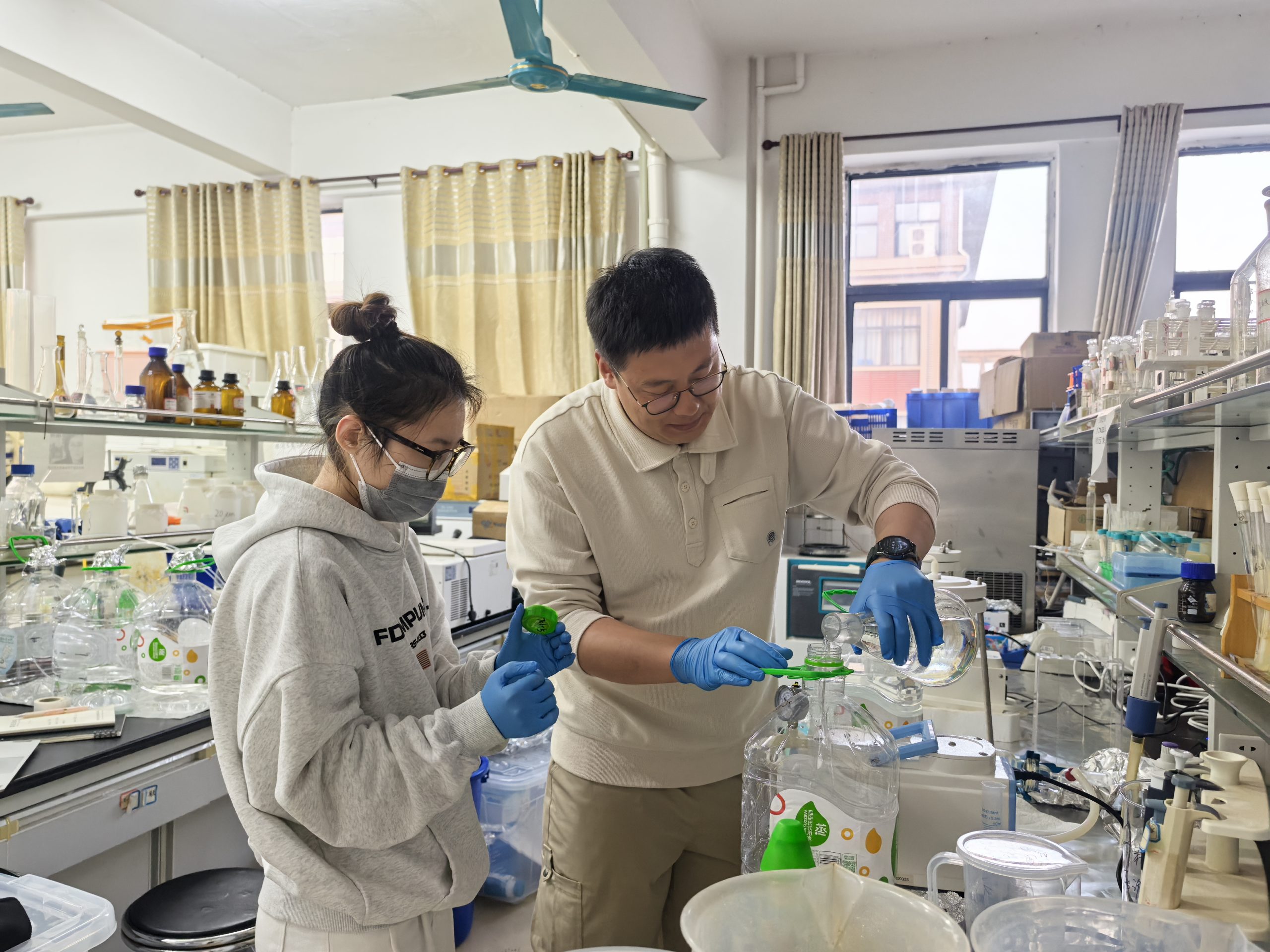
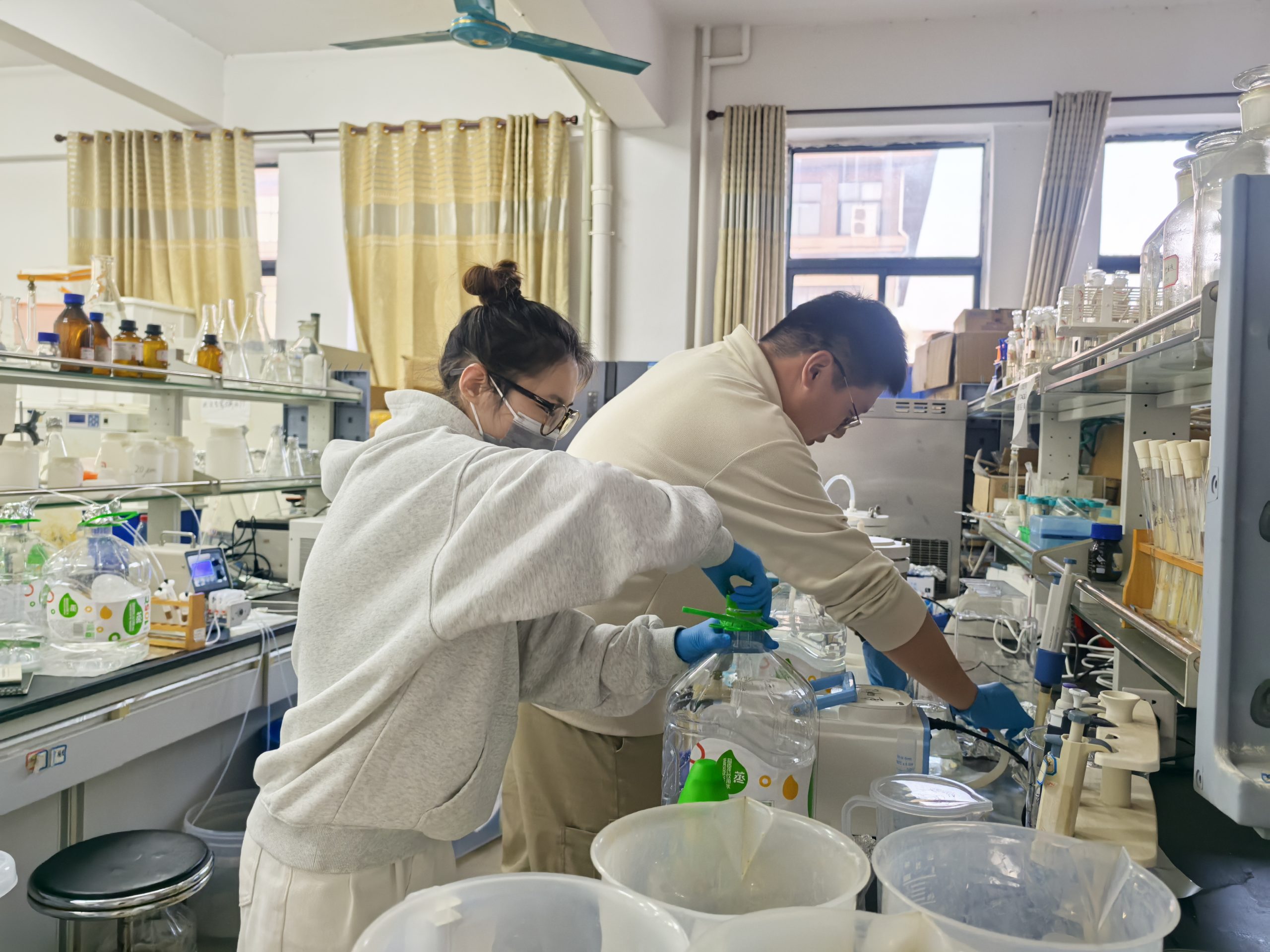
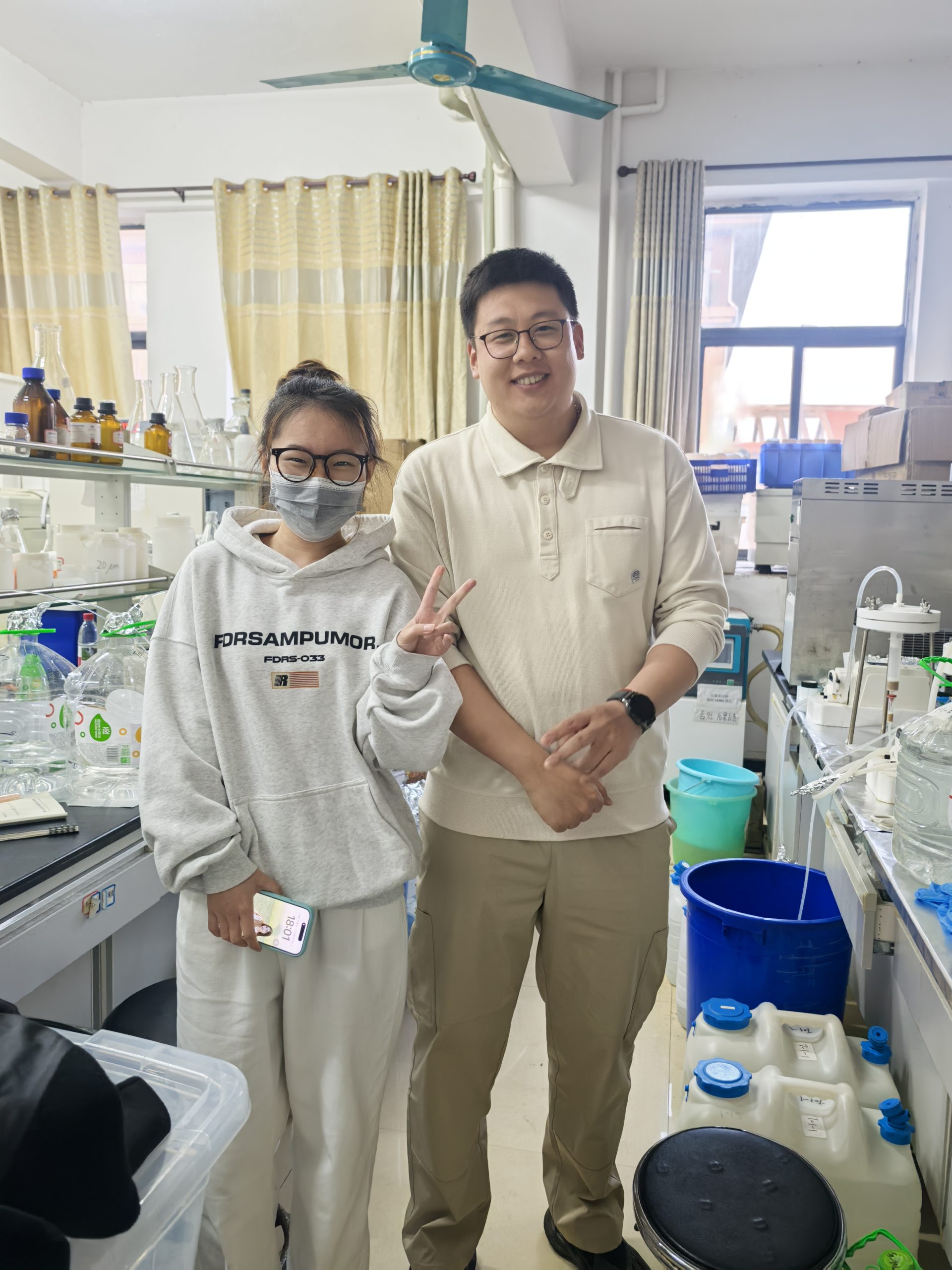
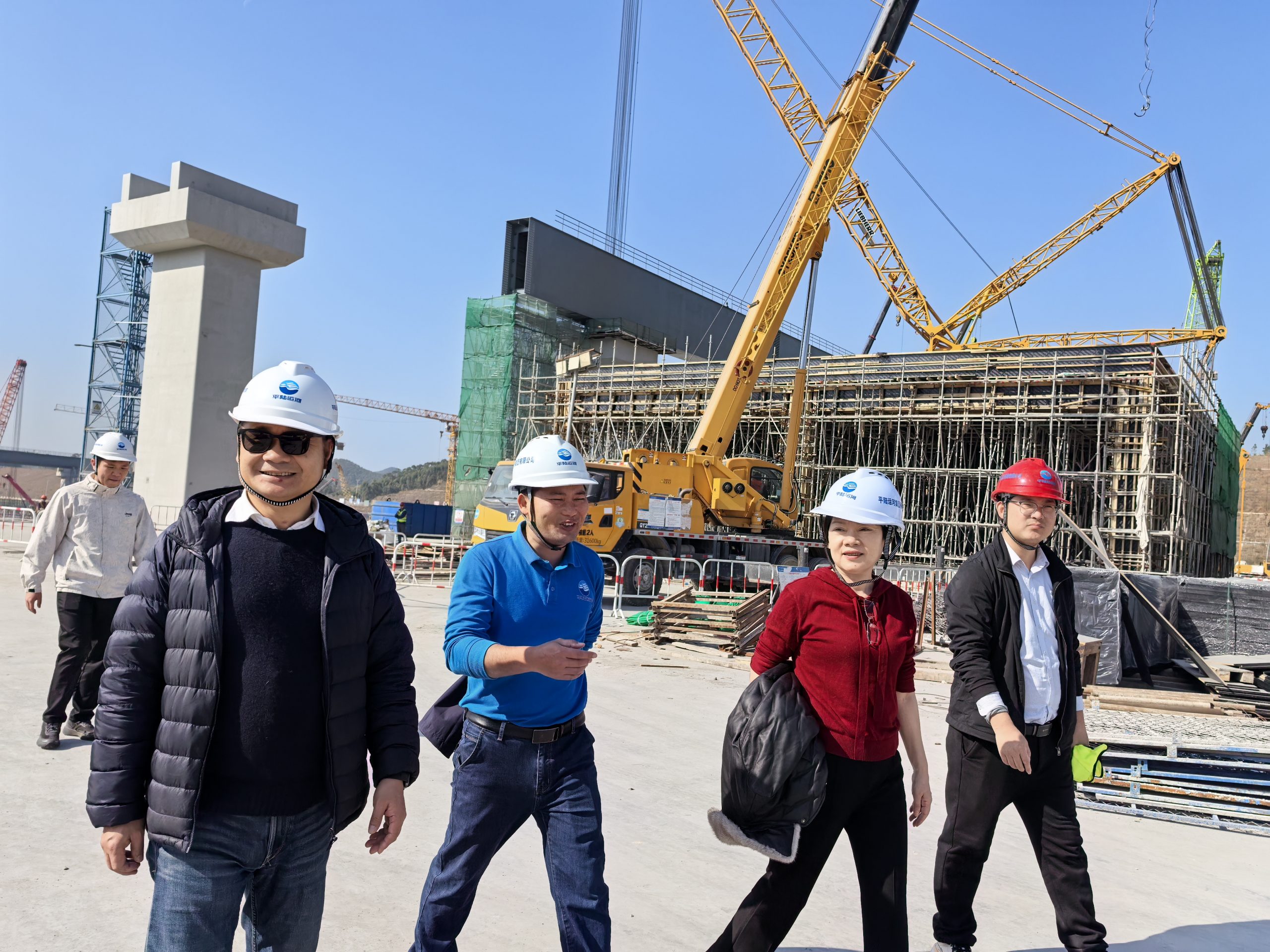
On January 11-12, Shizhen and Gan went to Beibu Gulf University (北部湾大学)in Qinzhou (钦州) for the annual meeting of the Field Station of Pinglu Canal (平陆运河河口海湾生态系统野外科学观测研究站), amid which Zhizhen was able to see Xuelin(雪琳) and Hangyi(航毅) who were working in the lab of the university for pretreatment of our water samples collected from the coast of Beibu Bay. Both of them had been working very hard in the lab and Hanyi also on the sampling boat. We met as well Professors Wang Yinghui (王英辉) of Guangxi University and Tang Jianhui (唐朝辉)of Yantai Institute of Coastal Zone CAS, and jointly visited the Centaury Project of Pinglu Canal (平陆运河). It is very excited for us to meet occasionally there!