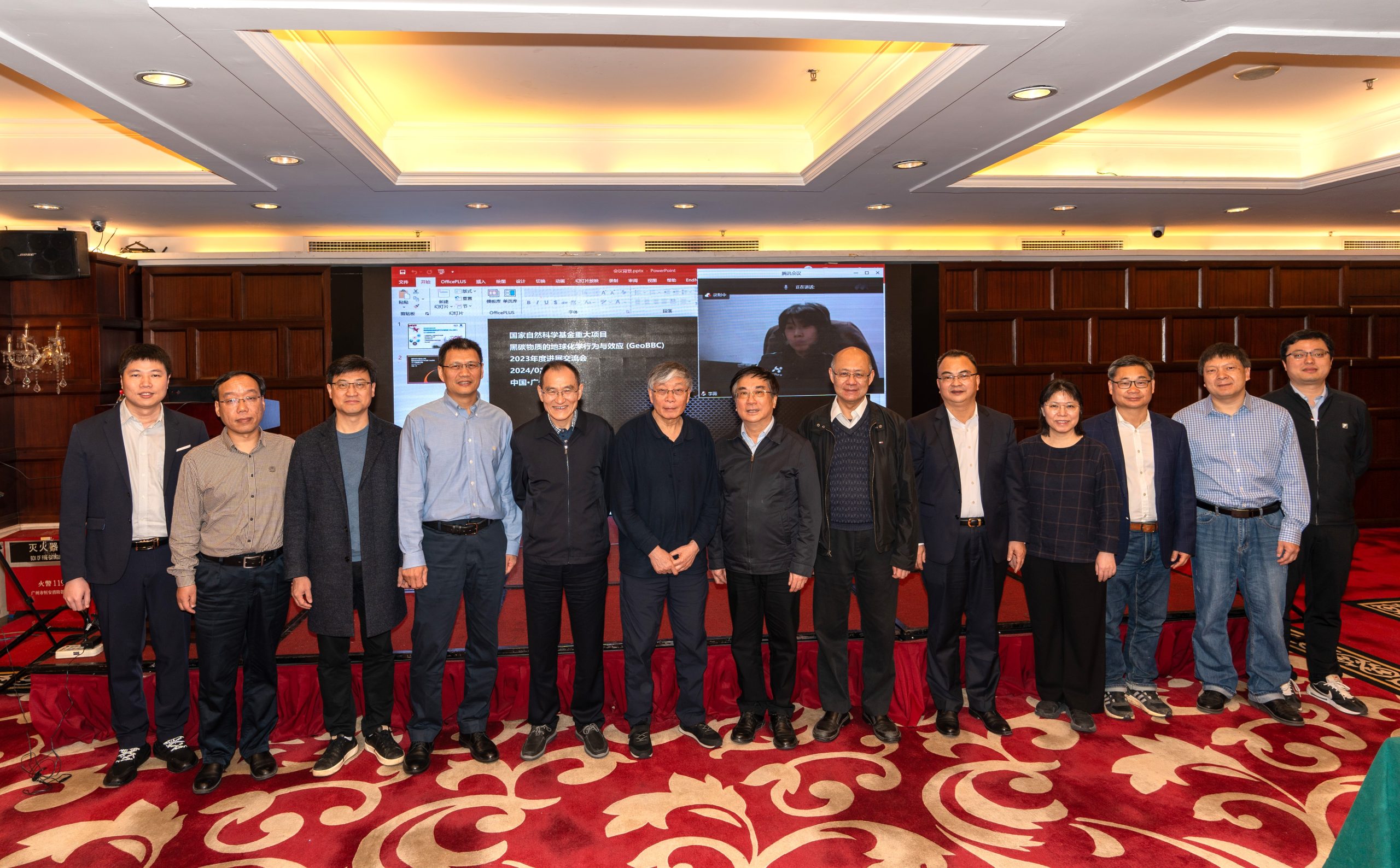
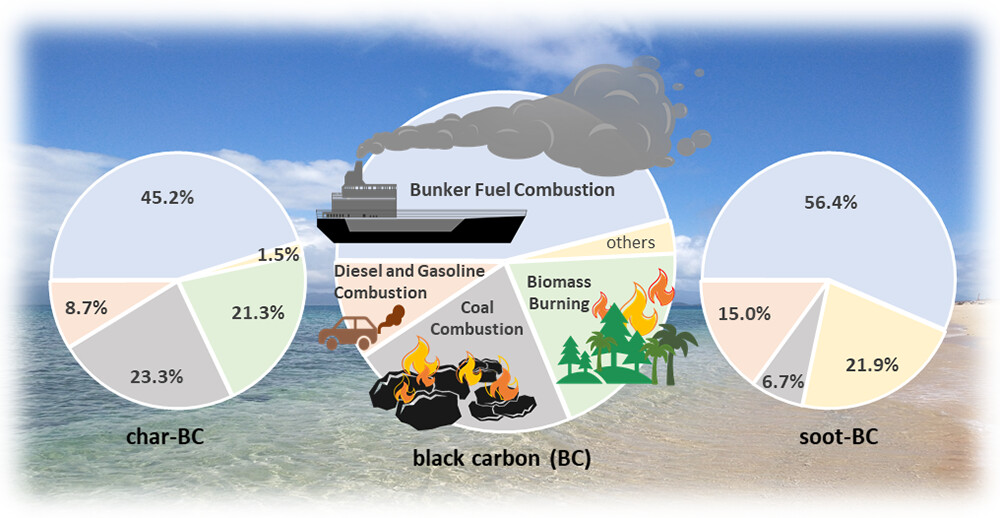
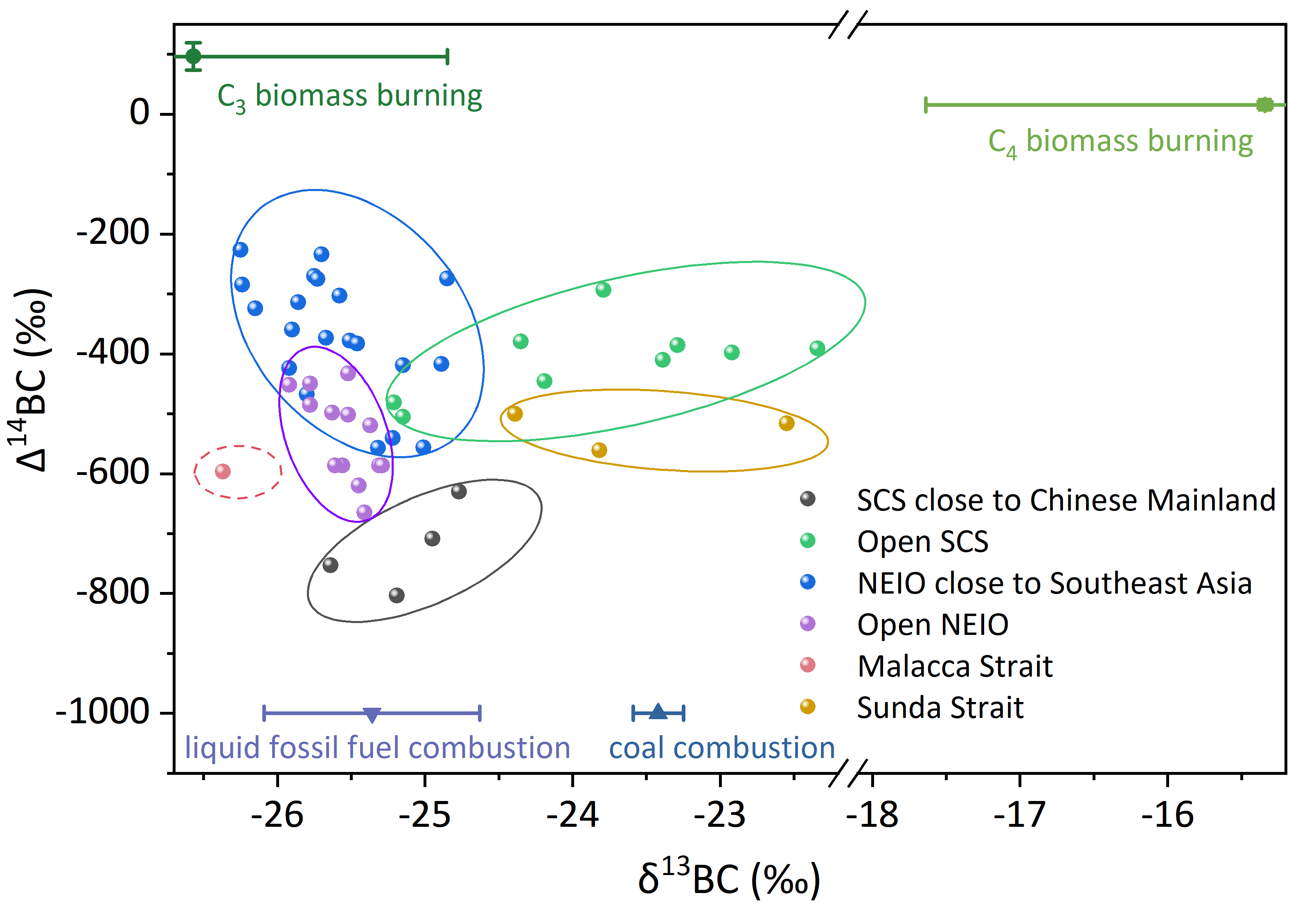
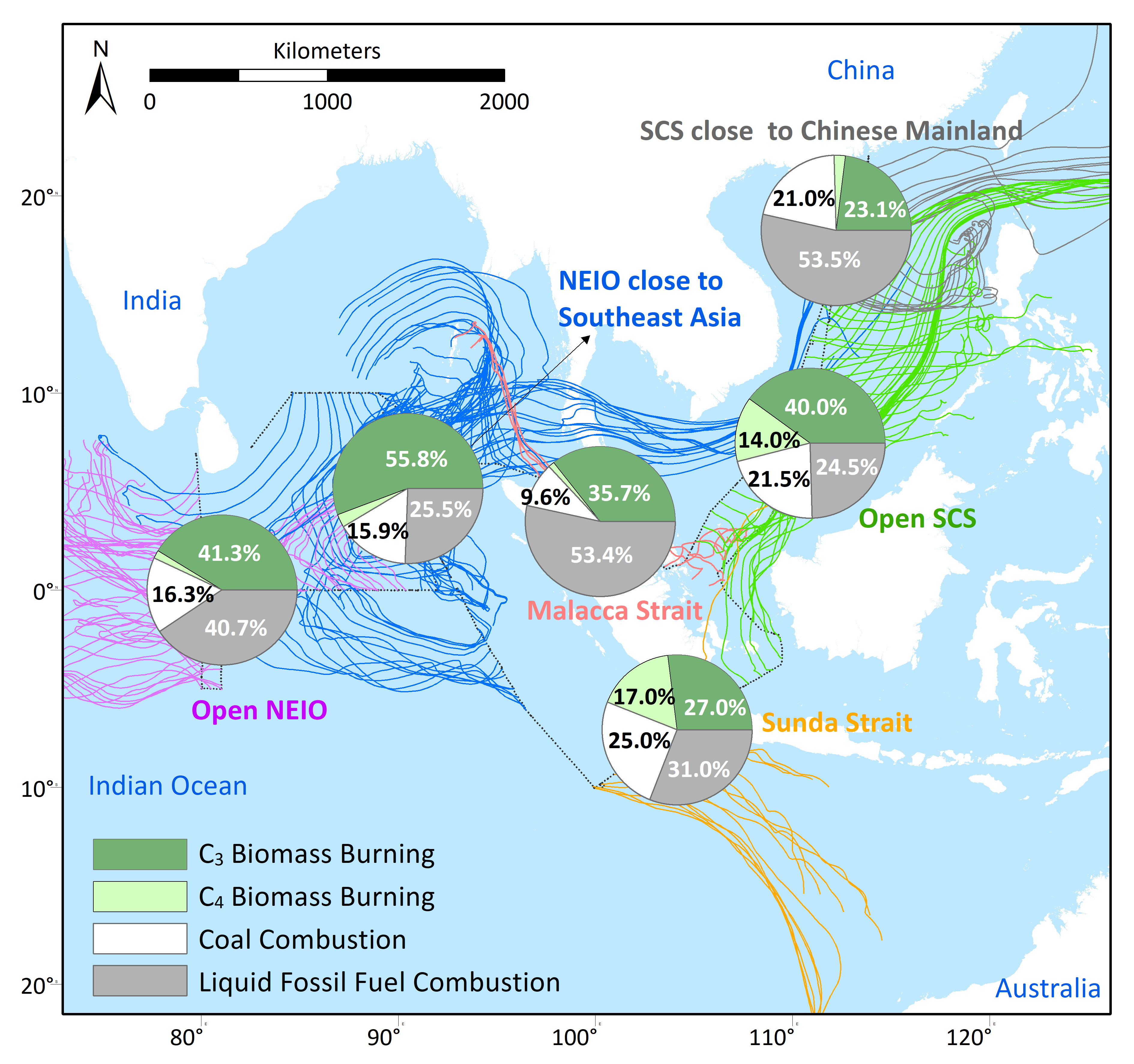
On the 16 -17th of January 2024, the 2023 annual meeting on “Black Carbon: Geochemical fate and environmental effects (GeoBBC)”, a major program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC), was held at the Jiayi International Hotel in Guangzhou.
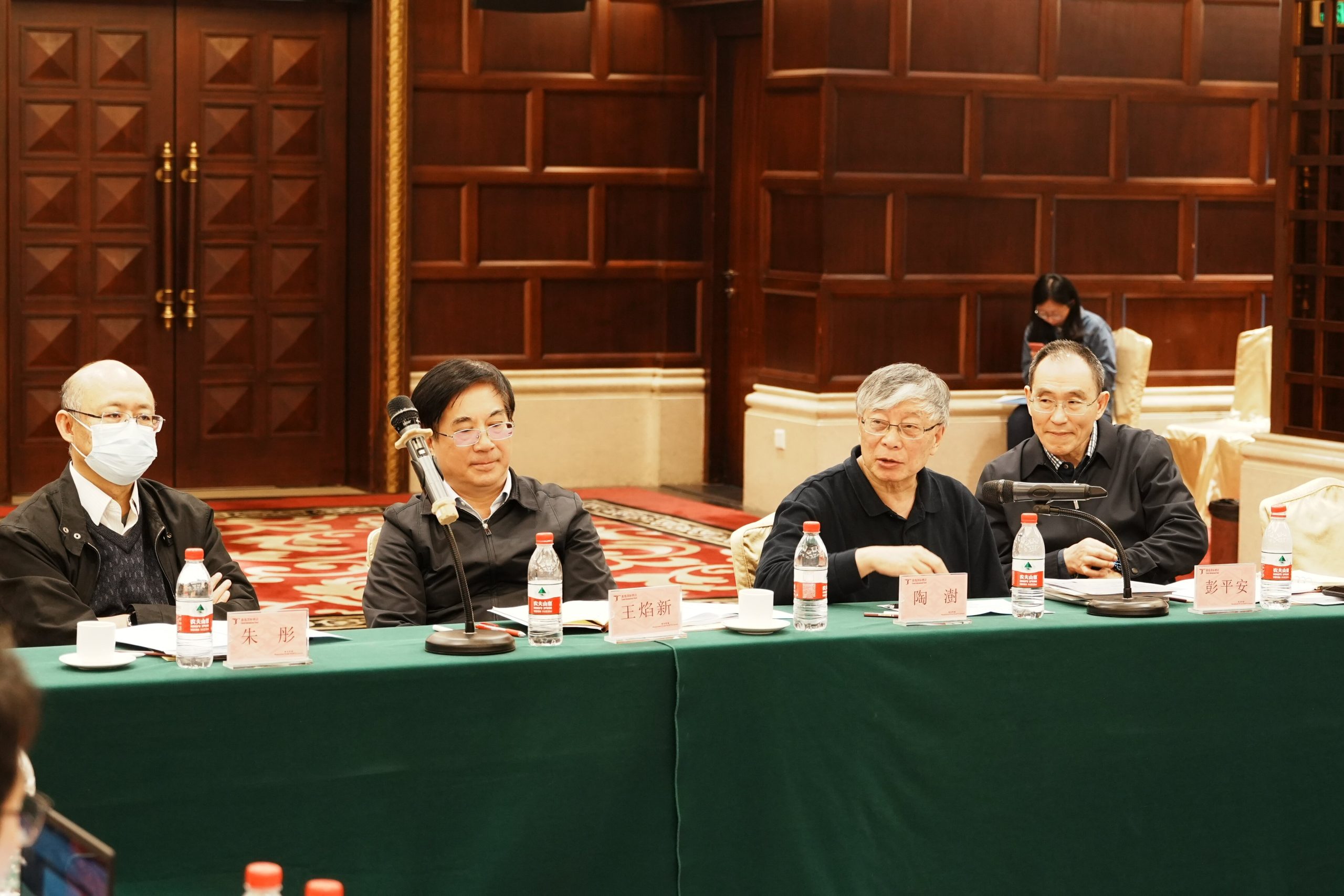
Li Wei (李薇), Deputy Director of the Department of Earth Sciences of NSFC, Academician Tao Shu (陶澍) from Peking University/Southern University of Science and Technology, Academician Peng Ping’an (彭平安) from Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences (GIG), Academician Wang Yanxin (王焰新) from China University of Geosciences (CUG), Academician Zhu Tong (朱彤) of Peking University, Professors Pan Bo (潘波) of Kunming University of Technology, Zhu Dongqiang (朱东强) and Zheng Mei (郑玫) of Peking University, and Chen Yingjun (陈颖军) of Fudan University attended the meeting as seering committee members. Professor/academician He Hongping (何宏平), Director of GIG, Tian Hui (田辉), Director of Science and Technology Department of GIG, and Zhang Gan (张干), chief scientist of the major project, as well as the project leaders and backbones attended the meeting.
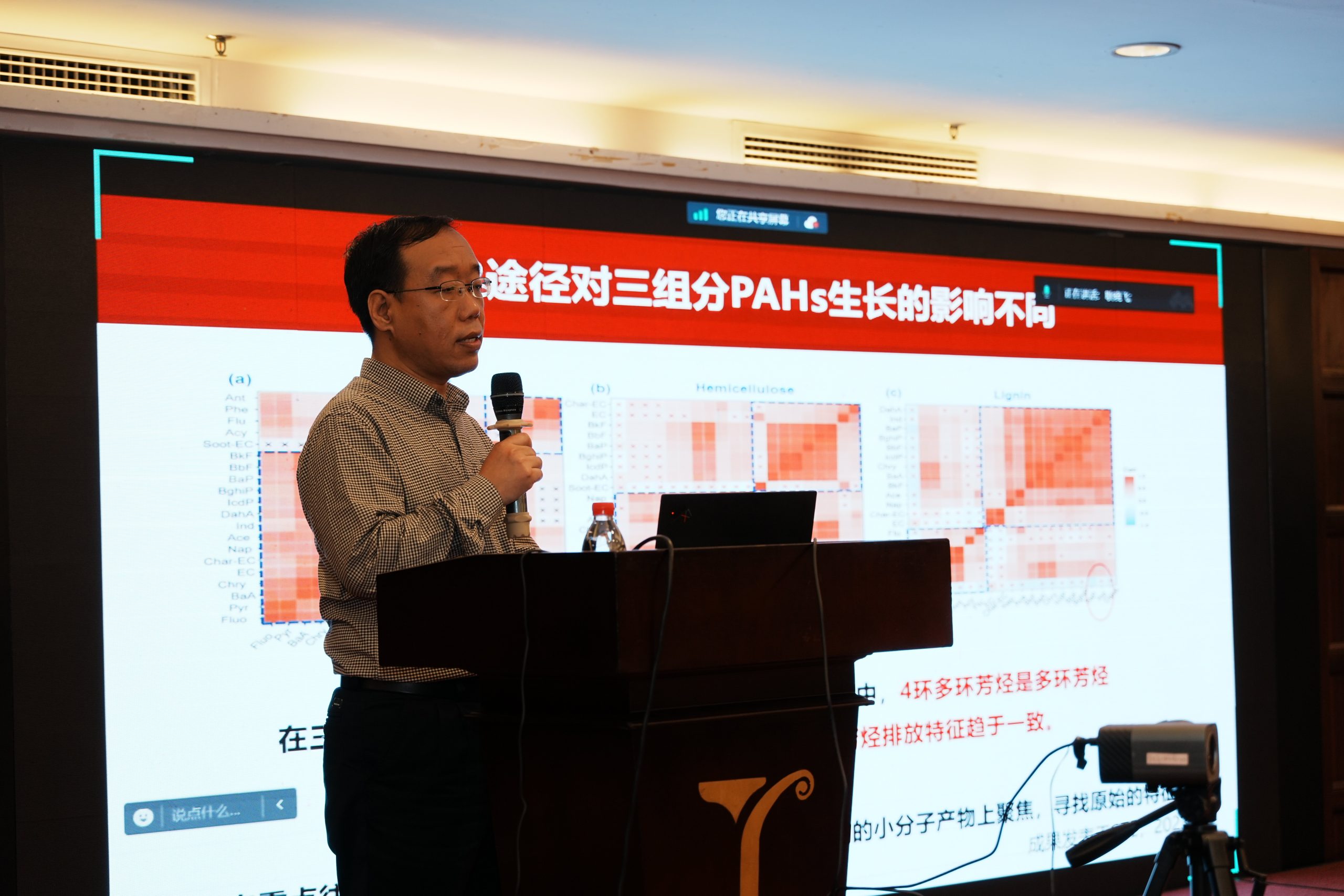
The opening ceremony of the conference was chaired by Tian Hui and a welcome speech was delivered by He Hongping. In her speech, Li Wei addressed that the major project was approved in 2021 and started in 2022. The project has been running for two years, with outstanding works, rich achievements and good progress. In addition, Li Wei suggested that the project should further be in line with the national demand and the “dual-carbon” strategy, strengthen target-oriented design, and face mid-term inspections. Zhang Gan gave a general introduction to the project from the aspects of project background, major research progress in 2023, and research plan for 2024. Then Song Jianzhong, Zhang Yanlin and Wang Junjian reported the annual progress of each sub-project, respectively.
The steering committee members fully agreed with the importance of the project. At the same time, constructive suggestions were made in terms of research scopes, innovative breakthroughs and project integrity, followed by in-depth discussions among the project leaders and backbone members. In response to the questions and suggestions raised by the attending experts, the project leaders and key members had a lively exchange and discussion, which helps with the next-year research plan.